Gulf Creek Copper
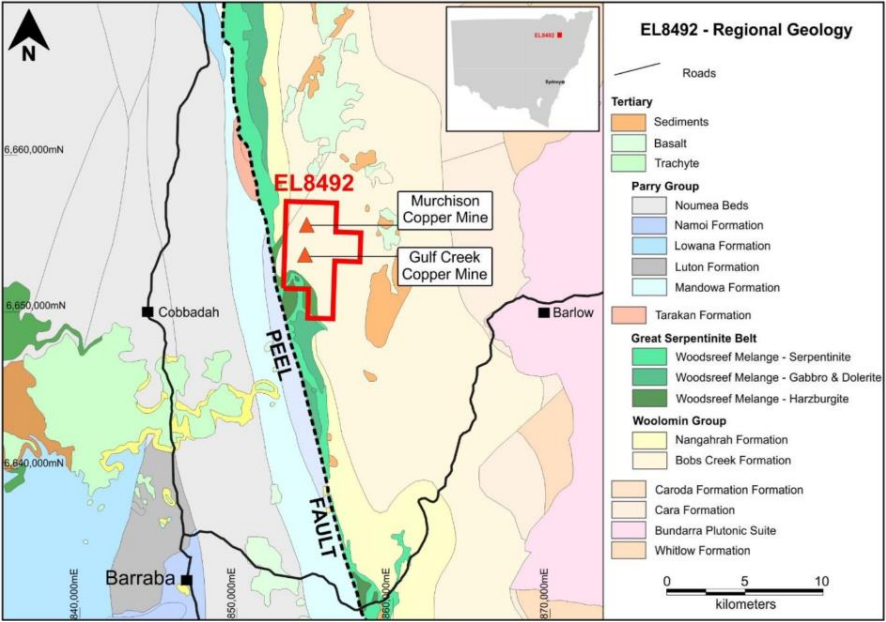
The Gulf Creek Copper project is located approximately 540km north of Sydney and ~400km from the Port of Newcastle. The Project is predominantly on private agricultural land and vacant crown land. The project lies within the footprint of the historic Gulf Creek copper mine, which was mined for copper ore between 1896 and 1912. Remarkably, the mine has had no modern concerted regional soil geochemistry, electromagnetics and drilling, having only two drill holes ever documented over its footprint. The historic Murchison Copper mine is also located within the north of the exploration lease, this mine is associated with magnetic stratigraphy and reports of >4% Cu.
High-grade copper-zinc mine virtually untouched since 1910 with potential repeat structures.
- High Grade Copper – Zinc VMS style deposit
- Mined over 100 years ago (1896-1912) with +100m vertical and +300m strike
- Only 2 holes ever drilled back in the 1960’s
- Successful Phase 1 program, fully permitted to drill Phase 2 to expand on the Phase 1 program
- Mineralisation connected with Magnetite which shows repeat structures to the north and west
- Potential of >3km of untested strike
Regional Setting for Classic VMS
- Classic setting for Cyprus Style Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Deposit (VMS)1
- Silurian-Devonian age geologically comparable to Woodlawn Deposit (>20Mt @ 1.6% Cu, 9.1% Zn endowment)2 owned by Develop Global Ltd
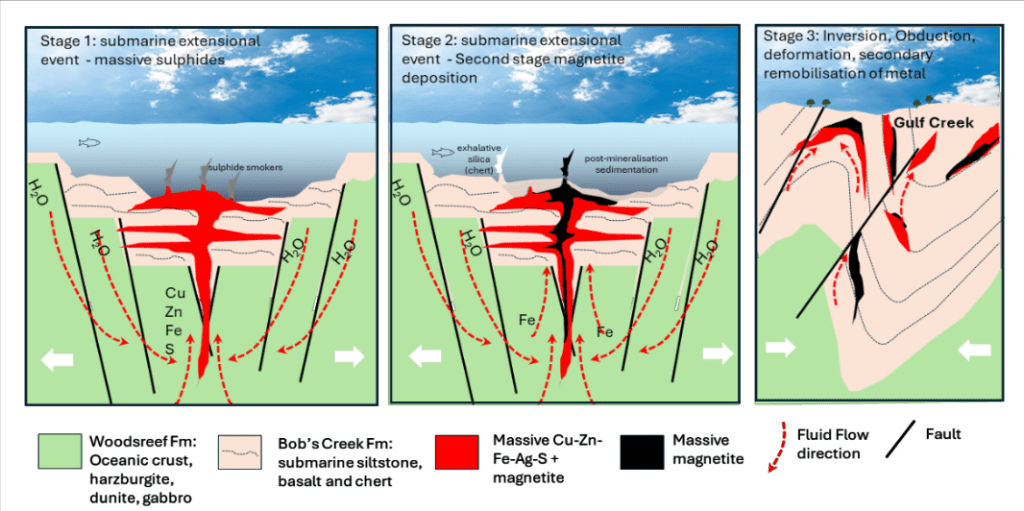
- Potentially comparable deposit refer to: Yildirim, Y et al. A magnetite-rich Cyprus-type VMS deposit in Ortaklar: A unique VMS style in the Tethyan metallogenic belt, Gaziantep, Turkey, Ore Geology Reviews. 79 (2016)
- https://portergeo.com.au/database/mineinfo.asp?mineid=mn295
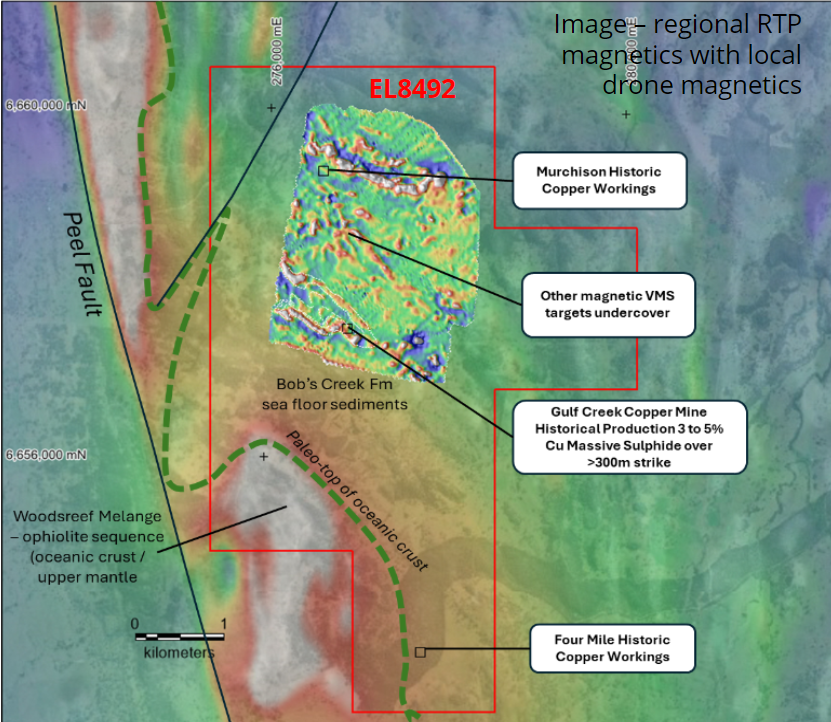
Extensional Exploration
- Strong association of magnetite with massive sulphide units as reported by UNE Thesis1
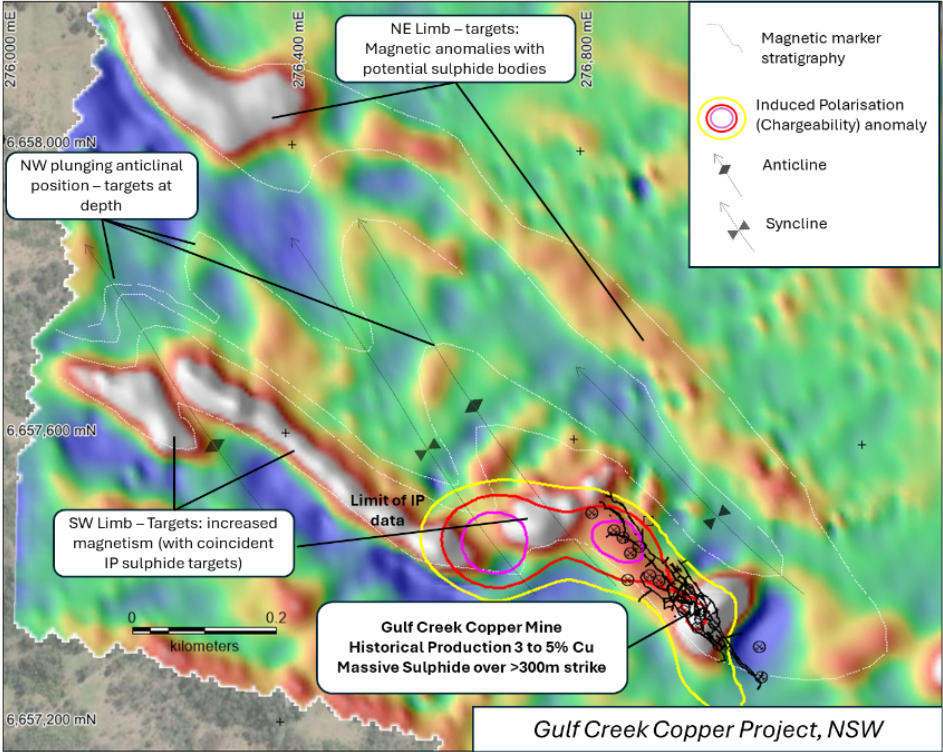
- 2021 drone magnetics matches known mineralization over >340m strike-length of historic ore-body
- IP Chargeability geophysics coincident with extensional magnetic targets
- Extended magnetic survey indicates a series of NW plunging folds providing >3km of local strike length of target magnetite-VMS target horizon within the Gulf Creek Syncline
- J. McCarron,. The Geochemistry of Silurian/Devonian Cherts of Djungati Terrane, NSW and their Implications for Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide Deposits. 1991. University of New England, Armidale, NSW, Hons Thesis
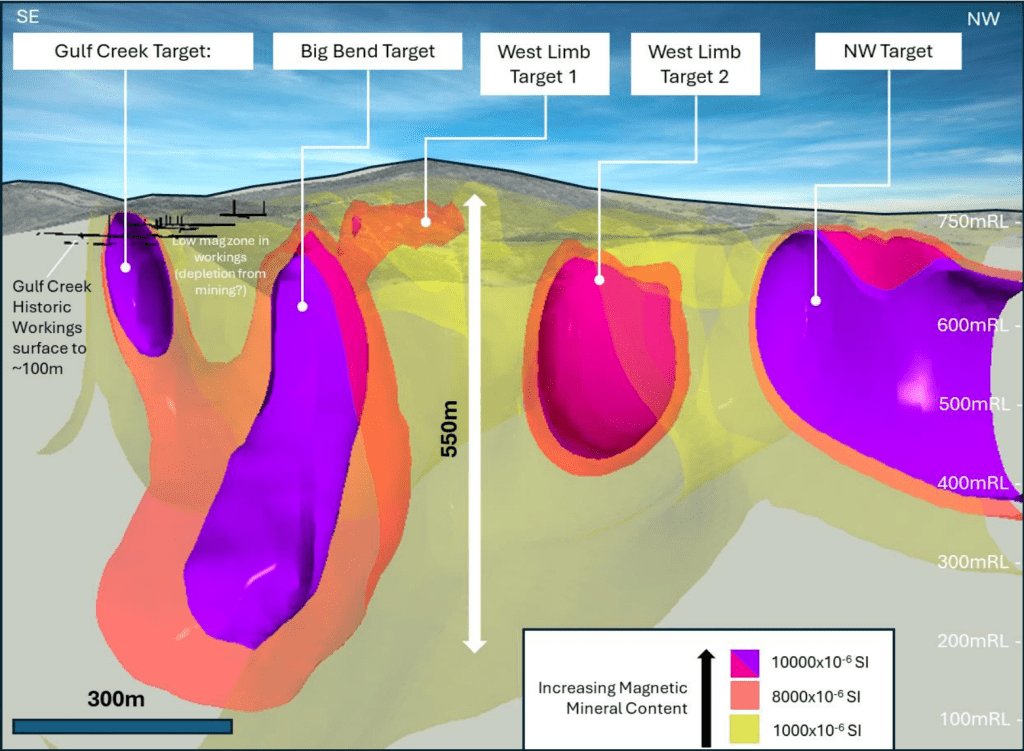
VMS Systems Known For Repeat Structures
- Big Bend Target:
- Very strong magnetism – typical of massive magnetite-sulphide
- Strong IP chargeability (sulphide indicator)
- Modelled from 50 to >550m
- No drilling ever
- Soils: Cu-Ag-Ce-Zn VMS association
- West Limb Targets:
- Strong magnetism in similar fold structures
- Soils: Cu-Ba-Be-Ce-Co VMS association
- Northwest Target:
- Strongest magnetic target in area
- 400x100m footprint – open to NW
- Modelling extends from near-surface to >400m
- Magnetic target in a small topographic low – no outcrop (missed by old-timers)
- Excellent soil anomaly adjacent: Cu-Co-Ag-Be-Ce-Zn VMS association